The Land of Canaan holds a significant place in biblical history, representing a region of promise and divine covenant. Today, understanding where Canaan is located involves exploring both its ancient boundaries and its modern equivalents. This article will delve into the historical and biblical definitions of Canaan, identify the modern countries that encompass this ancient land, and discuss the cultural and religious significance of Canaan in contemporary contexts. By examining these aspects, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of Canaan‘s relevance today and its impact on faith communities.
What Is the Historical and Biblical Definition of the Land of Canaan?
Canaan is defined in biblical texts as the land promised to the descendants of Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob. This region is often associated with the concept of a “Promised Land,” rich in resources and spiritual significance. The biblical narrative describes Canaan as a land flowing with milk and honey, symbolizing abundance and divine favor. The historical significance of Canaan extends beyond its geographical boundaries; it represents a pivotal point in the narrative of the Israelites and their covenant with God.
Further insights into the geographical context of biblical narratives underscore the profound connection between the physical landscape and the unfolding divine story.
How Is Canaan Described in Biblical Texts?
In the Bible, Canaan is described through various passages that highlight its fertility and strategic importance. Key verses, such as Genesis 12:1-3, emphasize God’s promise to Abraham regarding this land. Interpretations of Canaan‘s significance often focus on its role as a place of divine encounter and the fulfillment of God’s promises to His people. The descriptions found in the scriptures paint a vivid picture of a land that is not only physically rich but also spiritually vital.
What Were the Ancient Boundaries of Canaan?
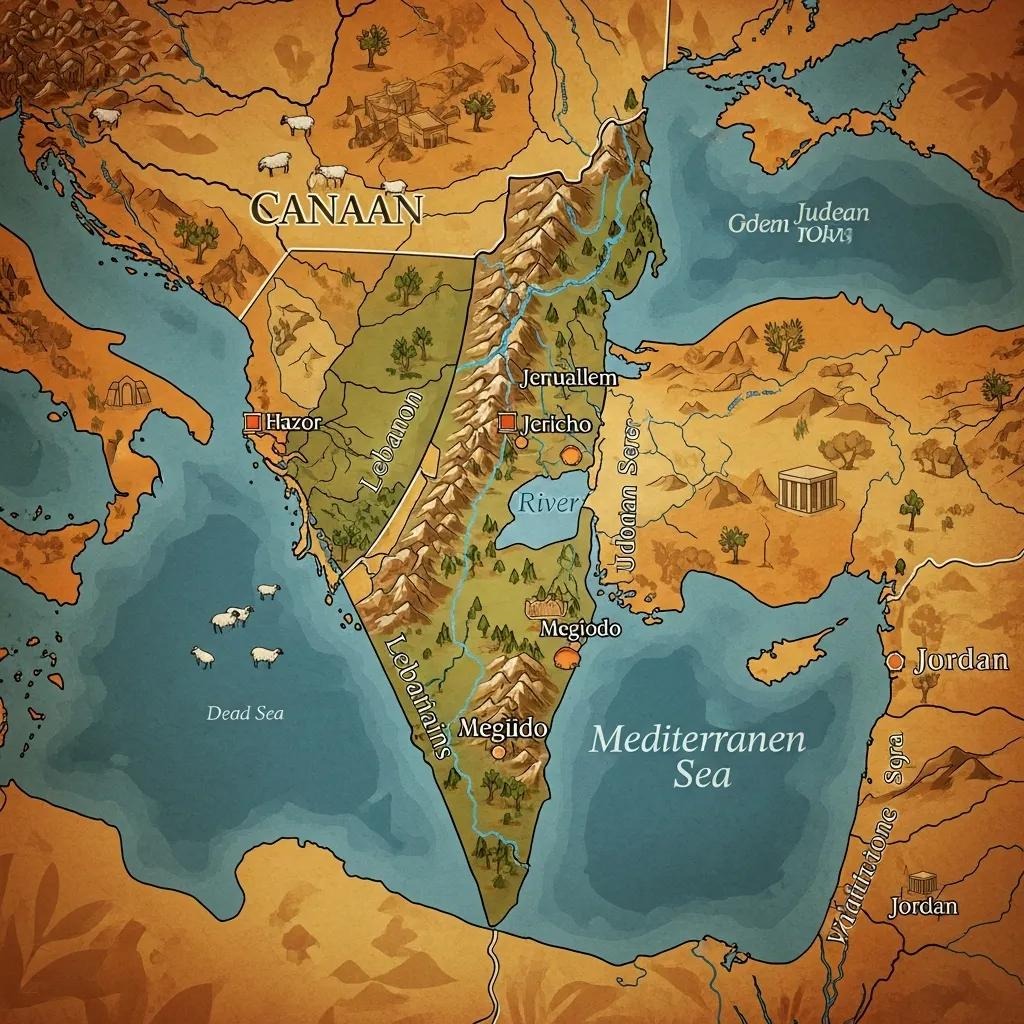
The ancient boundaries of Canaan are often debated among scholars, but they generally include regions that correspond to modern-day Israel, Palestine, Lebanon, and parts of Jordan and Syria. Historical maps and archaeological findings provide insights into these boundaries, illustrating how they have shifted over time. Understanding these ancient borders helps contextualize the biblical narrative and its implications for the people of Israel.
The complex and evolving concept of the Promised Land, with its geographical, theological, and historical dimensions, continues to influence contemporary religious and political narratives.
Which Modern Countries Cover the Region Known as Ancient Canaan?
Today, the region known as ancient Canaan encompasses several modern countries, each with its own historical and cultural ties to this biblical land.
How Do Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, and Palestine Relate to Ancient Canaan?
Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, and Palestine all share historical connections to ancient Canaan. Each of these countries contains areas that were once part of Canaan, contributing to a rich tapestry of cultural and religious heritage. The historical ties between these nations and the biblical narrative of Canaan highlight the ongoing significance of this region in contemporary discussions about identity and faith.
What Is the Connection Between the Levant Region and Canaan?
The Levant region, which includes modern-day Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, and Palestine, is often associated with Canaan due to its geographical and cultural similarities. The Levant serves as a bridge between different civilizations and has been a crossroads of trade, culture, and religion throughout history. This connection underscores the importance of Canaan in understanding the broader historical context of the Levant and its impact on modern societies.
Where Are Key Canaanite Cities Located in Today’s Geography?
Several ancient Canaanite cities have modern counterparts that continue to thrive today.
What Is the Modern Location of Ancient Jericho and Other Canaanite Cities?
Jericho, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, is located in the West Bank and is often identified as a key Canaanite city. Other significant cities, such as Hazor and Megiddo, also have modern locations that reflect their ancient roots. These cities serve as important archaeological sites, providing insights into the life and culture of the Canaanites.
How Do Archaeological Findings Map to Modern Sites?
Archaeological findings in the region have mapped ancient Canaanite cities to their modern counterparts, revealing layers of history that inform our understanding of the past. Excavations in places like Jericho and Megiddo have uncovered artifacts that illustrate the daily lives, religious practices, and societal structures of the Canaanites. These findings not only enrich our historical knowledge but also connect contemporary communities to their ancient heritage.
How Does the Biblical Land of Canaan Map Compare to Modern Maps?
The comparison between ancient maps of Canaan and modern maps reveals significant changes in geographical understanding and territorial claims.
What Are the Visual Differences Between Ancient and Modern Boundaries?
Visual comparisons of ancient and modern maps show how the boundaries of Canaan have evolved over time. Ancient maps often depict a more fluid understanding of territory, influenced by the movements of peoples and the establishment of new nations. In contrast, modern maps reflect fixed national borders that can obscure the historical significance of the land.
How Can Maps Help Understand the Promised Land Today?
Maps serve as valuable tools for understanding the Promised Land today, illustrating both the historical context and the contemporary geopolitical landscape. They can help individuals visualize the connections between ancient narratives and modern realities, fostering a deeper appreciation for the land’s significance in biblical history and its ongoing relevance in faith communities.
What Is the Cultural and Religious Significance of Canaan in Today’s Context?

Canaan‘s cultural and religious significance continues to resonate in contemporary society, influencing various faith communities and their practices.
How Does Canaanite Culture Influence Modern Faith Communities?
Canaanite culture has left a lasting impact on modern faith communities, particularly within Christianity and Judaism. Elements of Canaanite religious practices and societal structures can be seen in the rituals and traditions of these faiths. This cultural heritage enriches the spiritual lives of believers, connecting them to their historical roots.
Why Is the Land of Canaan Important for Contemporary Biblical Study?
The land of Canaan remains a focal point for contemporary biblical study, offering insights into the historical context of scripture. Scholars and theologians explore Canaan‘s significance to better understand the narratives of the Bible and their implications for modern faith. This ongoing exploration highlights the relevance of Canaan in discussions about spirituality, identity, and community.
| Modern Country | Ancient Canaan Connection | Cultural Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Israel | Central to biblical narratives | Birthplace of Judaism and Christianity |
| Palestine | Home to key biblical sites | Ongoing cultural and religious heritage |
| Lebanon | Historical trade routes | Influence on ancient Canaanite culture |
| Jordan | Part of the Promised Land | Rich archaeological sites |
| Syria | Northern boundary of Canaan | Historical conflicts and cultural ties |
Canaan‘s historical and cultural legacy remains vital in understanding the complexities of modern faith and identity. As we explore the land of Canaan today, we uncover layers of meaning that enrich our spiritual journeys through FaithTime devotional app and deepen our connections to the past.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does Canaan play in modern religious practices?
Canaan continues to play a significant role in modern religious practices, particularly within Judaism and Christianity. Many rituals and traditions are rooted in the historical narratives associated with Canaan, such as the Passover in Judaism, which commemorates the Israelites‘ exodus from Egypt and their journey to the Promised Land. In Christianity, Canaan symbolizes spiritual fulfillment and divine promise, influencing worship and teachings. This ongoing connection to Canaan enriches the spiritual lives of believers, fostering a sense of continuity with their faith’s historical roots.
How do modern political issues relate to the historical significance of Canaan?
The historical significance of Canaan is deeply intertwined with contemporary political issues in the region. The land’s biblical narratives and its designation as the Promised Land have influenced national identities and territorial claims, particularly in Israel and Palestine. These historical ties often complicate modern geopolitical discussions, as various groups seek to assert their connection to the land based on religious and cultural heritage. Understanding Canaan‘s historical context is essential for navigating these complex political landscapes and fostering dialogue among different communities.
What archaeological discoveries have been made in Canaan’s modern territories?
Numerous archaeological discoveries in modern territories of Canaan have provided valuable insights into ancient civilizations. Excavations in cities like Jericho, Megiddo, and Hazor have unearthed artifacts, structures, and inscriptions that illuminate the daily lives, religious practices, and societal structures of the Canaanites. These findings not only enhance our understanding of the historical context of the Bible but also connect contemporary communities to their ancient heritage, revealing the continuity of human experience across millennia.
How does the concept of the Promised Land influence interfaith dialogue?
The concept of the Promised Land significantly influences interfaith dialogue, particularly among Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Each faith has its interpretation of Canaan‘s significance, which can lead to both common ground and points of contention. Understanding these diverse perspectives fosters respectful discussions about heritage, identity, and spirituality. By exploring the shared narratives surrounding Canaan, interfaith dialogue can promote mutual respect and understanding, encouraging collaboration on issues of peace and coexistence in the region.
What educational resources are available for studying Canaan’s history?
There are numerous educational resources available for studying Canaan‘s history, including books, academic journals, and online courses. Institutions like universities and theological seminaries often offer programs focused on biblical studies, archaeology, and Middle Eastern history. Additionally, museums in the region provide exhibitions and artifacts related to Canaanite culture. Online platforms, such as educational websites and digital libraries, also offer access to scholarly articles and lectures, making it easier for individuals to explore Canaan‘s rich historical and cultural legacy.
How can maps enhance our understanding of Canaan’s historical context?
Maps are invaluable tools for enhancing our understanding of Canaan‘s historical context. They visually represent the geographical boundaries and significant locations mentioned in biblical texts, allowing for a clearer comprehension of the land’s significance. By comparing ancient maps with modern ones, we can observe how territorial claims and cultural landscapes have evolved over time. This visual approach helps contextualize the narratives of the Bible within the physical geography of the region, fostering a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of history and faith.


